Contents
Why Utility Infrastructure Matters
Utility infrastructure is the backbone of modern communities, providing essential services like electricity, water, and communication systems. Properly designed and maintained, it supports daily life, drives economic activity, and ensures public safety. Even brief disruptions can create widespread challenges, from halting business operations to limiting access to healthcare and emergency response.
Building reliable utility infrastructure requires careful planning, the right tools, and strict adherence to safety practices. High-quality materials are equally important, as they help systems withstand environmental stress and long-term use. For instance, working with a dependable PVC conduit supplier ensures electrical wiring remains protected, reducing the risk of damage and outages. Together, these practices create resilient networks that serve communities effectively.
Overview of Key Tools and Equipment
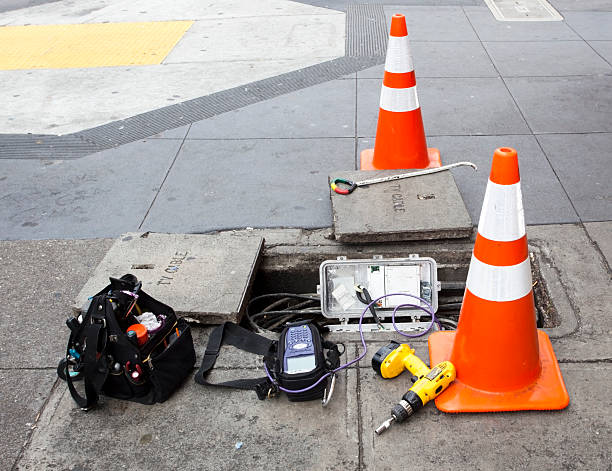
Utility professionals rely on a comprehensive toolkit to build and maintain service networks. For overhead lines, hot sticks allow crews to safely perform repairs on energized equipment, while hydraulic crimpers provide secure electrical connections. Underground systems depend on digger derricks for drilling, cable pullers for installation, and specialized diagnostic tools for pinpointing faults. Companies must procure the right gear for efficiency and safety, choosing reputable sources for everything from test equipment to physical conduits.
The utility landscape also demands that crews are equipped for diverse environments, whether scaling poles in remote areas or threading cables beneath busy city streets. Efficiency is further enhanced by using advanced measuring tools such as phasing meters and ground resistance testers. Access to accurate, timely information saves time, reduces risk, and keeps service interruptions to a minimum.
Safety Standards and Guidelines
Utility work is classified among the most hazardous professions. To mitigate risks, strict safety standards govern every stage of utility construction and maintenance. Regulatory bodies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandate use of personal protective equipment, proper lockout/tagout procedures, and systematic equipment inspections.
Many organizations exceed these minimum requirements by fostering a culture of safety. Regular safety briefings, clear emergency protocols, and investment in high-visibility gear protect both crews and the surrounding public. Improving safety practices is crucial, especially as utilities address increasingly complex grid systems.
Training and Skills in the Utility Industry
Specialized knowledge and hands-on skills are prerequisites for working with utility infrastructure. Workers complete rigorous training programs encompassing technical, mechanical, and safety competencies before ever heading into the field. This education covers not only proper tool use and PPE but also first aid, electrical theory, and emergency response tactics.
Most utilities require ongoing training to keep crews up-to-date on evolving industry standards and emerging hazards. Providers frequently partner with accredited organizations and safety consultants, ensuring that certification remains current and workers are equipped for daily tasks and rare emergencies.
Emerging Technologies in Utilities
Technology accelerates change in the utility industry, with drones performing rapid inspections of overhead lines to detect faults, and IoT devices enabling real-time system monitoring for predictive maintenance and remote troubleshooting. Digital platforms support compliance documentation, scheduling, and tracking materials. Companies are integrating augmented reality for field training and complex repairs, allowing workers to practice virtually and improve readiness. As these tools evolve, utilities can boost efficiency and service continuity.
Future Trends in Utility Tools and Safety
The utility sector is poised to widely adopt smart, integrated technologies. Cloud-based platforms promise to further automate inspection data, compliance paperwork, and asset management. Ergonomically designed tools help reduce fatigue and prevent repetitive injuries, advancing worker safety and productivity.
Sustainability is rising as a priority. Eco-friendly materials and less energy-intensive equipment manufacturing processes will continue gaining traction, supporting regulatory compliance and environmental responsibility. To stay ahead, utility companies must remain agile, incorporating best practices and adapting to industry innovations as they arrive.
Final Insights
Utility infrastructure is the backbone of modern society, requiring reliable materials, skilled workers, and strict safety practices to function effectively. Continuous adaptation ensures resilience and progress as technology and sustainability reshape the industry. By combining innovation with responsibility, utilities can safeguard communities today while preparing for the demands of tomorrow.