Today, more people seek solutions for healthier homes that also reduce the environmental impact of pest treatments. While cleaning helps maintain health, proactive pest management prevents infestations and health risks. Relying only on chemical controls overlooks the benefits of an integrated approach. IPM offers a comprehensive, prevention-focused approach that considers pest life cycles and environmental interactions. This reduces chemical use, creates a safer home, and supports public health goals, with agencies like the EPA promoting IPM as a key technique. Consequently, IPM is becoming the new standard in responsible pest control.
Contents
Understanding Integrated Pest Management
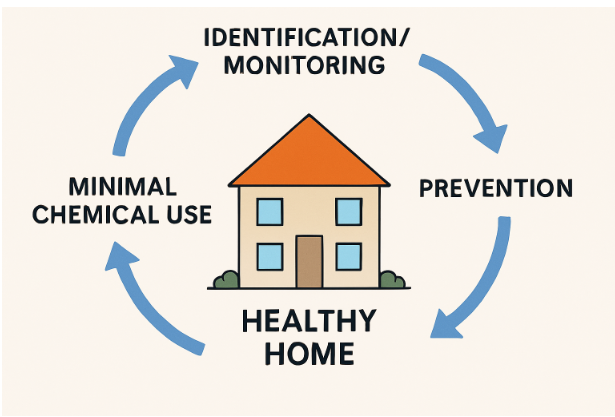
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an environmentally friendly approach to pest control that combines prevention, monitoring, and targeted actions. Partnering with a pest control company in Sudbury can help homeowners and businesses implement effective IPM strategies tailored to their specific needs. Unlike traditional methods that focus on chemical extermination, IPM emphasizes understanding pest biology to use the least intervention necessary, balancing effectiveness with safety for humans, pets, and beneficial species. The EPA emphasizes IPM as crucial for minimizing pesticide risks. It involves a series of steps to manage pests early, aiming to control populations rather than eliminating every pest, making it both practical and sustainable.
Key Components of IPM
Effective Integrated Pest Management (IPM) strategies comprise a structured approach that encompasses several critical steps. First, accurate identification and monitoring of pests are crucial, enabling targeted and necessary interventions. Second, setting action thresholds helps determine when pest populations require control, preventing excessive treatments and focusing on the most pressing issues. Third, preventive measures such as crop rotation, sealing entry points, removing food sources, and enhancing sanitation are essential to reduce the risk of infestations and disrupt pest life cycles before they reach problematic levels. Finally, suppose monitoring reveals that preventive strategies are insufficient. In that case, IPM advocates for utilizing the least disruptive control methods first, such as mechanical traps or biological agents, resorting to the application of chemical pesticides only when necessary.
Benefits of Implementing IPM
Adopting Integrated Pest Management (IPM) offers substantial long-term benefits for individuals, families, and communities in several key areas. Firstly, it enhances environmental protection by safeguarding vital pollinators and minimizing the contamination of water, air, and soil, thereby fostering a healthier ecosystem for both humans and wildlife. Secondly, IPM contributes to health safety by reducing unnecessary exposure to pesticides, thereby lowering the risk of adverse health effects, particularly for vulnerable groups such as children, pregnant women, and pets. Lastly, the economic advantages of IPM are noteworthy; it emphasizes prevention and addresses only confirmed pest issues, which leads to lower overall expenditure on pest control. The result is fewer pests, reduced damage, and minimized costly repairs over time.
Practical Steps to Implement IPM at Home
Homeowners interested in Integrated Pest Management (IPM) can take several practical steps to control pests effectively. First, sealing entry points is crucial; this involves filling gaps around doors, windows, and foundations to prevent pests from gaining access to the home. Second, maintaining cleanliness is essential; regular cleaning of kitchens, bathrooms, and food storage areas helps eliminate food sources for pests. Additionally, proper waste management is essential—garbage should be disposed of promptly in sealed containers, and compost or recycling should be kept at a distance from the house. Finally, homeowners should monitor for pest activity regularly by conducting checks for droppings, gnaw marks, or nests, enabling early detection and resolution of pest issues.
Technological Advancements in IPM
Technology is rapidly enhancing the effectiveness and reach of IPM programs. In agriculture, relay intercropping—a technique where crops are deliberately planted to boost populations of beneficial insects—has emerged as a means of biological pest suppression, demonstrating the versatility of IPM solutions.
Challenges and Considerations
While Integrated Pest Management (IPM) provides significant advantages, it also presents several challenges. Firstly, effective implementation necessitates a comprehensive understanding of pest identification, biology, and behavior, which often requires continuous education or professional advice. Secondly, successful IPM emphasizes prevention and monitoring, leading to a greater initial time commitment compared to traditional, reactive pest control methods. Lastly, although preventative strategies and non-chemical solutions can result in long-term savings, they may entail initial costs for tools, exclusion materials, or professional evaluations.
Conclusion
Integrated Pest Management delivers a comprehensive, science-based path to healthier homes and communities. By focusing on prevention, prompt action, and minimal chemical use, IPM reduces health and environmental risks while providing cost-effective pest control. Whether you are a homeowner, a school administrator, or a community leader, embracing IPM strategies promotes safe and thriving living environments for everyone.